NHP Quick Start
A locally built Docker debugging environment, simulating nhp-server, nhp-ac, traefik, web-app, etc. This environment can be used for:
- Quickly understanding how opennhp works
- Plugin debugging
- Basic logic validation
- Partial performance stress testing
1. Overview
This Quick Start guide helps developers rapidly set up the OpenNHP Docker environment, build the source code, and test key features of OpenNHP. Whether you’re exploring how OpenNHP makes servers “invisible” to unauthorized scans or integrating it into existing Zero Trust architectures, this guide provides the essential steps to get you up and running quickly.
1.1 Network Topology
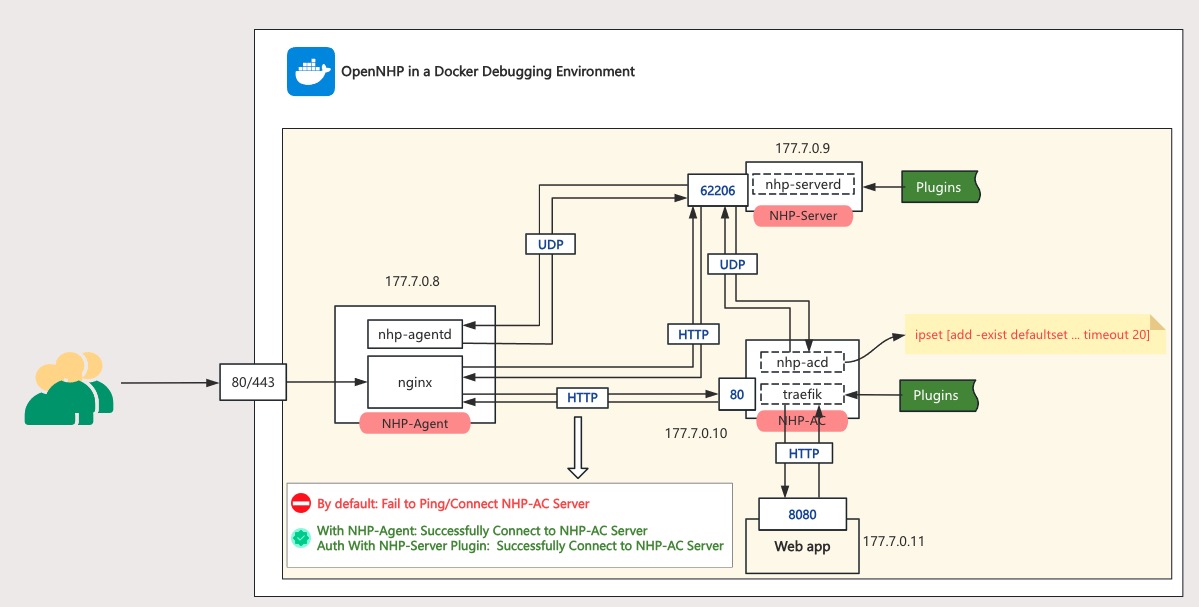
| Container Name | IP | Description |
|---|---|---|
| NHP-Agent | 177.7.0.8 | Runs nhp-agentd & nginx (both disabled by default). Port mapping: 443→AC:80, 80→NHP-Server:62206 |
| NHP-Server | 177.7.0.9 | Runs nhp-serverd with exposed port 62206 |
| NHP-AC | 177.7.0.10 | Runs nhp-acd & traefik. All ports blocked by default |
| Web App | 177.7.0.11 | Protected web application. Only allows NHP-AC access on port 8080 |
1.2 Test Scenarios
| State | Expected Result |
|---|---|
| Scenario 1 | Invisibility (for unauthorized users), Ping or direct access to NHP-AC Server’s proxied Web-app fails |
| Scenario 2 | After “knocking” via NHP-Agent, can successfully access the NHP-AC protected Web-app |
| Scenario 3 | After web identity authentication “knock”, can successfully access the NHP-AC protected Web-app |
2. Installing Docker Environment
2.1 Docker Desktop for Mac
brew install --cask docker
Alternative: Download the .dmg package directly from Docker’s official website: https://www.docker.com/products/docker-desktop/
2.2 Docker Desktop for Windows
- System Requirements:
- Windows 10/11 (64-bit, Pro/Enterprise/Home editions)
- WSL 2 enabled (recommended) or Hyper-V
- Installation Steps:
- Download Docker Desktop from the official website
- Run the installer and follow the setup wizard
Launch Docker Desktop after installation completes
3. Building base images from Source Code
3.1 Clone the latest code
git clone https://github.com/OpenNHP/opennhp.git
3.2 Quick Start Script (Recommended)
The easiest way to build and manage the Docker environment is using the quick_start.sh script:
cd ./docker
# Run the interactive menu
./quick_start.sh
# For users in China, use --china flag to enable mirrors
./quick_start.sh --china
The script provides an interactive menu with the following options:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Build ALL and Start (Recommended for first-time users) |
| 2 | Build Base Image (opennhp-base) |
| 3 | Build NHP-Server |
| 4 | Build NHP-AC |
| 5 | Build NHP-Agent |
| 6 | Build Web-App |
| 7 | Start All Services |
| 8 | Stop All Services |
| 9 | Restart All Services |
| 10-12 | View Logs (nhp-server/nhp-ac/nhp-agent) |
| 13 | Clean Docker Images |
| 14 | Clean ALL (images + volumes + networks) |
| 15 | Toggle China Mirror |
3.3 Manual Build: opennhp-base Docker Image
If you prefer manual commands:
cd ./docker
docker build --no-cache -t opennhp-base:latest -f Dockerfile.base ..
Build Arguments:
You can override GO_VERSION and GOPROXY by adding build arguments:
# For users in China, use goproxy.cn and mirrors.aliyun.com for faster downloads
docker build --build-arg GOPROXY=https://goproxy.cn,direct --build-arg APT_MIRROR=mirrors.aliyun.com --no-cache -t opennhp-base:latest -f Dockerfile.base ..
# To specify a different Go version (default: 1.25.6)
docker build --build-arg GO_VERSION=1.25.6 --no-cache -t opennhp-base:latest -f Dockerfile.base ..
Troubleshooting - BuildKit Builder Issue:
If docker compose build fails with error like pull access denied, repository does not exist, it may be because your Docker is using a docker-container buildx builder which cannot access local images. Fix it by switching to the default builder:
# Check current builder
docker buildx ls
# Switch to docker driver builder
docker buildx use desktop-linux
# or
docker buildx use default
4. Running and Testing the Environment
The following startup command will build nhp-server, nhp-ac, web-app, and nhp-agent images during the startup process.
4.1 Start All Services
Using quick_start.sh (Recommended):
cd ./docker
./quick_start.sh # Select option [7] Start All Services
./quick_start.sh --china # For users in China
Using docker compose directly:
cd ./docker
docker compose up -d
For users in China, pass GOPROXY and APT_MIRROR environment variables for faster builds:
GOPROXY=https://goproxy.cn,direct APT_MIRROR=mirrors.aliyun.com docker compose up -d
4.2 Scenario 1: Invisibility (for unauthorized users)
Enter the nhp agentd container for verification
cd ./docker
docker exec -it nhp-agent bash
By default, the following error occurs when using curl NHP-AC (under protection)
root@68a230812459:/workdir# curl -i http://177.7.0.10
curl: (28) Failed to connect to 177.7.0.10 port 80: Connection timed out
Port scan verification, enter the NHP Agent container and install nmap
root@ee88ec992447:/# docker exec -it nhp-agent bash
root@ee88ec992447:/# apt-get update && apt-get install -y nmap
Scanning NHP-AC through NHP-Agent cannot detect any ports
root@ee88ec992447:/# nmap 177.7.0.10
Starting Nmap 7.93 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2025-07-03 07:33 UTC
Nmap scan report for nhp-ac.docker_nginx (177.7.0.10)
Host is up (0.000044s latency).
All 1000 scanned ports on nhp-ac.docker_nginx (177.7.0.10) are in ignored states.
Not shown: 1000 filtered tcp ports (no-response)
MAC Address: 12:B4:5C:EB:72:F4 (Unknown)
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 21.84 seconds
4.3 Scenario 2: Using nhp-agentd service to knock on the door
After starting the nhp agentd service with the command nohup /nhp-agent/nhp-agentd run 2>&1 &, the access is normal as follows:
root@68a230812459:/workdir# nohup /nhp-agent/nhp-agentd run 2>&1 &
root@6e21724b68f1:/workdir# curl -i http://177.7.0.10
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Length: 26
Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf-8
Date: Tue, 08 Jul 2025 06:21:10 GMT
{"message":"Hello World!"}
When NHP agent starts, it can scan to port 80 of NHP-AC
root@ee88ec992447:/# nmap 177.7.0.10
Starting Nmap 7.93 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2025-07-03 07:37 UTC
Nmap scan report for nhp-ac.docker_nginx (177.7.0.10)
Host is up (0.000094s latency).
Not shown: 999 filtered tcp ports (no-response)
PORT STATE SERVICE
80/tcp open http
MAC Address: 12:B4:5C:EB:72:F4 (Unknown)
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 4.96 seconds
4.4 Scenario 3: Using simulated authorization service login to verify
Stop the nhp-agentd service and start nginx in the NHP-Agent container
root@6e21724b68f1:/workdir# ps -aux|grep nhp-agentd
root 38 0.3 0.2 1974072 20448 pts/0 Sl 02:55 0:00 /nhp-agent/nhp-agentd run
root 51 0.0 0.0 2844 1424 pts/0 S+ 02:55 0:00 grep --color=auto nhp-agentd
root@6e21724b68f1:/workdir# kill 38
root@6e21724b68f1:/workdir# nginx
visit: http://localhost/plugins/example?resid=demo&action=login
- Expected page to display normally
- Visit before knocking on the door: https://localhost/ Timeout (504 Gateway Time out)
- Click login (after knocking on the door), the page will jump to normal and can be accessed normally https://localhost/ (Note: The opening time is 15 seconds, and access is prohibited after 15 seconds)
- In the NHP Agent container, use
curl - i http://177.7.0.10Can display content normally - When clicking on login (after knocking on the door), you can scan to port 80 of NHP-AC
root@ee88ec992447:/# nmap 177.7.0.10
Starting Nmap 7.93 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2025-07-03 07:37 UTC
Nmap scan report for nhp-ac.docker_nginx (177.7.0.10)
Host is up (0.000094s latency).
Not shown: 999 filtered tcp ports (no-response)
PORT STATE SERVICE
80/tcp open http
MAC Address: 12:B4:5C:EB:72:F4 (Unknown)
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 4.96 seconds
4.5 Verify if the ipset rules are effective
docker exec -it nhp-ac ipset list
After knocking on the door through nhp-agentd or authorized plugins, if the following result appears in NHP-AC’s ipset, it indicates that the rule was successfully written, which means that the knocking was successful: Name: defaultset Rules
Name: defaultset
Type: hash:ip,port,ip
Revision: 5
Header: family inet hashsize 1024 maxelem 1000000 timeout 120 counters
Size in memory: 656
References: 7
Number of entries: 2
Members:
177.7.0.8,udp:80,177.7.0.10 timeout 8 packets 0 bytes 0
177.7.0.8,tcp:80,177.7.0.10 timeout 8 packets 90 bytes 14565
Name: defaultset_down
Type: hash:ip,port,ip
Revision: 5
Header: family inet hashsize 1024 maxelem 1000000 timeout 121 counters
Size in memory: 208
References: 2
Number of entries: 0
Members:
Name: tempset
Type: hash:net,port
Revision: 7
Header: family inet hashsize 1024 maxelem 1000000 timeout 5 counters
Size in memory: 456
References: 2
Number of entries: 0
Members:
5. Edit the Code and Rebuild
After modifying the code, you can rebuild individual services or all services for debugging.
5.1 Code editing
You can use your IDE (such as VSCode) to open the project and modify the OpenNHP code.
5.2 Rebuild Using quick_start.sh (Recommended)
The quick_start.sh script provides the easiest way to rebuild services:
cd ./docker
./quick_start.sh # Interactive menu
./quick_start.sh --china # For users in China
| Option | Service | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 3 | nhp-server | Rebuild and restart NHP-Server |
| 4 | nhp-ac | Rebuild and restart NHP-AC |
| 5 | nhp-agent | Rebuild and restart NHP-Agent |
| 6 | web-app | Rebuild and restart Web-App |
| 1 | ALL | Full rebuild including base image |
5.3 Manual Rebuild Commands
If you prefer manual commands instead of using quick_start.sh:
cd ./docker
# Rebuild a specific service (replace SERVICE_NAME with: nhp-server, nhp-ac, nhp-agent, or web-app)
docker compose build --no-cache SERVICE_NAME
docker stop SERVICE_NAME && docker rm SERVICE_NAME
docker compose up -d SERVICE_NAME
# Rebuild all services
docker compose build --no-cache
docker compose down
docker compose up -d
For users in China, add environment variables:
cd ./docker
# Rebuild a specific service
GOPROXY=https://goproxy.cn,direct APT_MIRROR=mirrors.aliyun.com docker compose build --no-cache SERVICE_NAME
docker stop SERVICE_NAME && docker rm SERVICE_NAME
docker compose up -d SERVICE_NAME
# Rebuild all services
GOPROXY=https://goproxy.cn,direct APT_MIRROR=mirrors.aliyun.com docker compose build --no-cache
docker compose down
docker compose up -d
5.4 View Logs
Using quick_start.sh (options 10-12) or docker compose:
# View nhp-server logs
docker compose logs -f nhp-server
# View nhp-ac logs
docker compose logs -f nhp-ac
# View nhp-agent logs
docker compose logs -f nhp-agent
5.5 Clean Up
Using quick_start.sh (options 13-14) or manual commands:
# Remove all OpenNHP images
docker rmi opennhp-base:latest opennhp-server:latest opennhp-ac:latest opennhp-agent:latest web-app:latest
# Stop and remove containers, networks, volumes
docker compose down -v